Java 基础 - 反射
原文链接:Java 基础 - 反射机制详解
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,**对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性。**这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。Java反射机制在框架设计中极为广泛,需要深入理解。本文综合多篇文章后,总结了Java 反射的相关知识,希望可以提升你对Java中反射的认知效率。
1. 反射基础
RRIT(Run-Time Type Identification)运行时类型识别。在《Thinking in Java》一书第十四章中有提到,其作用是**在运行时识别一个对象的类型和类的信息。**主要有两种方式:一种是“传统的”RTTI,它假定我们在编译时已经知道了所有的类型;另一种是“反射”机制,它允许我们在运行时发现和使用类的信息。
反射就是把java类中的各种成分映射成一个个的Java对象。
例如:一个类有:成员变量、方法、构造方法、包等等信息,利用反射技术可以对一个类进行解剖,把个个组成部分映射成一个个对象。
这里我们首先需要理解 Class类,以及类的加载机制; 然后基于此我们如何通过反射获取Class类以及类中的成员变量、方法、构造方法等。
1.1 Class类
Class类,Class类也是一个实实在在的类,存在于JDK的java.lang包中。Class类的实例表示java应用运行时的类(class ans enum)或接口(interface and annotation)(每个java类运行时都在JVM里表现为一个class对象,可通过类名.class、类型.getClass()、Class.forName("类名")等方法获取class对象)。数组同样也被映射为为class 对象的一个类,所有具有相同元素类型和维数的数组都共享该 Class 对象。基本类型boolean,byte,char,short,int,long,float,double和关键字void同样表现为 class 对象。
某种意义上来说,Java有两种对象:实例对象和Class对象。
每个类的运行时的类型信息就是用Class对象表示的。它包含了与类有关的信息。
我们的实例对象就通过Class对象来创建的。Java使用Class对象执行其RTTI(运行时类型识别,Run-Time Type Identification),多态是基于RTTI实现的。
public final class Class<T> implements java.io.Serializable,
GenericDeclaration,
Type,
AnnotatedElement {
private static final int ANNOTATION= 0x00002000;
private static final int ENUM = 0x00004000;
private static final int SYNTHETIC = 0x00001000;
private static native void registerNatives();
static {
registerNatives();
}
/*
* Private constructor. Only the Java Virtual Machine creates Class objects. //私有构造器,只有JVM才能调用创建Class对象
* This constructor is not used and prevents the default constructor being
* generated.
*/
private Class(ClassLoader loader) {
// Initialize final field for classLoader. The initialization value of non-null
// prevents future JIT optimizations from assuming this final field is null.
classLoader = loader;
}到这我们也就可以得出以下几点信息:
Class类也是类的一种,与
class关键字是不一样的。手动编写的类被编译后会产生一个Class对象,其表示的是创建的类的类型信息,而且这个Class对象保存在同名.class的文件中(字节码文件)
每个通过关键字class标识的类,在内存中有且只有一个与之对应的Class对象来描述其类型信息,无论创建多少个实例对象,其依据的都是用一个Class对象。
Class类只存私有构造函数,因此对应Class对象只能有JVM创建和加载
Class类的对象作用是运行时提供或获得某个对象的类型信息,这点对于反射技术很重要(关于反射稍后分析)。
1.2 类加载
类加载机制和类字节码技术可以参考如下两篇文章:
源代码通过编译器编译为字节码,再通过类加载子系统进行加载到JVM中运行
这篇文章将带你深入理解Java 类加载机制
其中,这里我们需要回顾的是:
类加载机制流程
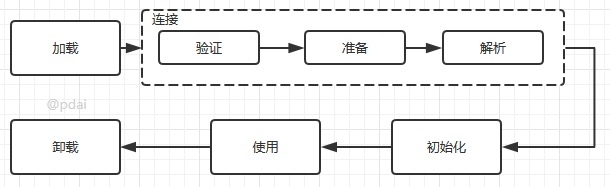
2021-03-01-yllbJ9 类的加载
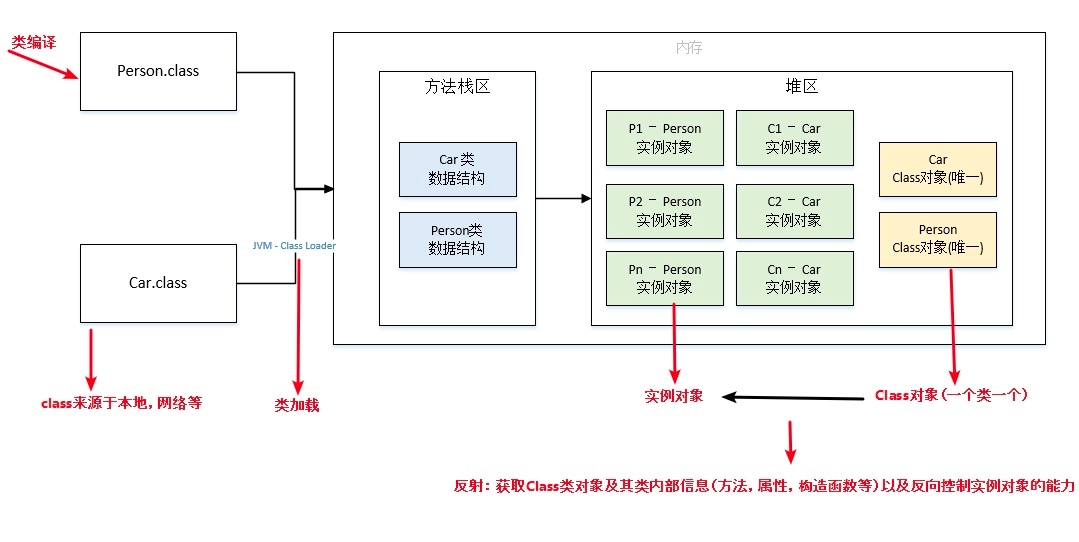
2021-03-01-UoBVaX 加载,这是由类加载器(ClassLoader)执行的。通过一个类的全限定名来获取其定义的二进制字节流(Class字节码),将这个字节流所代表的静态存储结构转化为方法去的运行时数据接口,根据字节码在Java堆中生成一个代表这个类的java.lang.Class对象。
在类加载阶段,类加载器首先检查这个类的Class对象是否已经被加载。如果尚未加载,默认的类加载器就会根据类的全限定名查找.class文件加载Class对象。在这个类的字节码被加载时,它们会接受验证,以确保其没有被破坏,并且不包含不良Java代码。一旦某个类的Class对象被载入内存,我们就可以它来创建这个类的所有对象。
链接。在链接阶段将验证Class文件中的字节流包含的信息是否符合当前虚拟机的要求,为静态域分配存储空间并设置类变量的初始值(默认的零值),并且如果必需的话,将常量池中的符号引用转化为直接引用。
初始化。到了此阶段,才真正开始执行类中定义的java程序代码。用于执行该类的静态初始器和静态初始块,如果该类有父类的话,则优先对其父类进行初始化。
2. 反射的使用
TIP
基于此我们如何通过反射获取Class类对象以及类中的成员变量、方法、构造方法等。
在Java中,Class类与java.lang.reflect类库一起对反射技术进行了全力的支持。在反射包中,我们常用的类主要有Constructor类表示的是Class 对象所表示的类的构造方法,利用它可以在运行时动态创建对象、Field表示Class对象所表示的类的成员变量,通过它可以在运行时动态修改成员变量的属性值(包含private)、Method表示Class对象所表示的类的成员方法,通过它可以动态调用对象的方法(包含private),下面将对这几个重要类进行分别说明。
2.1 获取Class类对象
在类加载的时候,jvm会创建一个class对象。
class对象是可以说是反射中最常用的,获取class对象的方式的主要有三种:
根据类名:
类名.class根据对象:
对象.getClass()根据全限定类名:
Class.forName(全限定类名)输出结果:
再来看看 Class类的方法
方法名说明forName()
(1)获取Class对象的一个引用,但引用的类还没有加载(该类的第一个对象没有生成)就加载了这个类。 (2)为了产生Class引用,forName()立即就进行了初始化。
Object-getClass()
获取Class对象的一个引用,返回表示该对象的实际类型的Class引用。
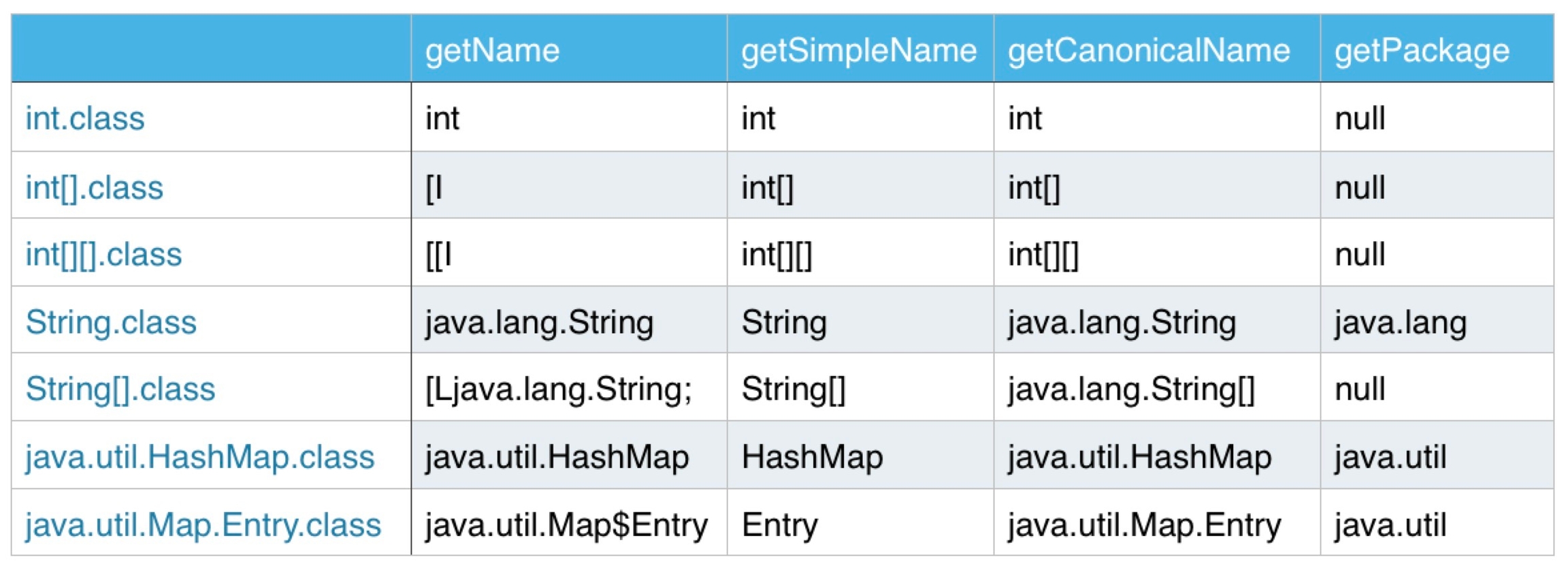
getName()
取全限定的类名(包括包名),即类的完整名字。
getSimpleName()
获取类名(不包括包名)
getCanonicalName()
获取全限定的类名(包括包名)
isInterface()
判断Class对象是否是表示一个接口
getInterfaces()
返回Class对象数组,表示Class对象所引用的类所实现的所有接口。
getSupercalss()
返回Class对象,表示Class对象所引用的类所继承的直接基类。应用该方法可在运行时发现一个对象完整的继承结构。
newInstance()
返回一个Oject对象,是实现“虚拟构造器”的一种途径。使用该方法创建的类,必须带有无参的构造器。
getFields()
获得某个类的所有的公共(public)的字段,包括继承自父类的所有公共字段。 类似的还有getMethods和getConstructors。
getDeclaredFields
获得某个类的自己声明的字段,即包括public、private和proteced,默认但是不包括父类声明的任何字段。类似的还有getDeclaredMethods和getDeclaredConstructors。
简单测试下(这里例子源于https://blog.csdn.net/mcryeasy/article/details/52344729)
getName、getCanonicalName与getSimpleName的区别:
getSimpleName:只获取类名getName:类的全限定名,jvm中Class的表示,可以用于动态加载Class对象,例如Class.forName。getCanonicalName:返回更容易理解的表示,主要用于输出(toString)或log打印,大多数情况下和getName一样,但是在内部类、数组等类型的表示形式就不同了。
2.2 Constructor类及其用法
Constructor类存在于反射包(java.lang.reflect)中,反映的是Class 对象所表示的类的构造方法。
获取Constructor对象是通过Class类中的方法获取的,Class类与Constructor相关的主要方法如下:
static Class<?>
forName(String className)
返回与带有给定字符串名的类或接口相关联的 Class 对象。
Constructor
getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes)
返回指定参数类型、具有public访问权限的构造函数对象
Constructor<?>[]
getConstructors()
返回所有具有public访问权限的构造函数的Constructor对象数组
Constructor
getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes)
返回指定参数类型、所有声明的(包括private)构造函数对象
Constructor<?>[]
getDeclaredConstructor()
返回所有声明的(包括private)构造函数对象
T
newInstance()
调用无参构造器创建此 Class 对象所表示的类的一个新实例。
下面看一个简单例子来了解Constructor对象的使用:
输出结果:
关于Constructor类本身一些常用方法如下(仅部分,其他可查API)
Class
getDeclaringClass()
返回 Class 对象,该对象表示声明由此 Constructor 对象表示的构造方法的类,其实就是返回真实类型(不包含参数)
Type[]
getGenericParameterTypes()
按照声明顺序返回一组 Type 对象,返回的就是 Constructor对象构造函数的形参类型。
String
getName()
以字符串形式返回此构造方法的名称。
Class<?>[]
getParameterTypes()
按照声明顺序返回一组 Class 对象,即返回Constructor 对象所表示构造方法的形参类型
T
newInstance(Object... initargs)
使用此 Constructor对象表示的构造函数来创建新实例
String
toGenericString()
返回描述此 Constructor 的字符串,其中包括类型参数。
代码演示如下:
输出结果:
2.3 Field类及其用法
Field 提供有关类或接口的单个字段的信息,以及对它的动态访问权限。反射的字段可能是一个类(静态)字段或实例字段。
同样的道理,我们可以通过Class类的提供的方法来获取代表字段信息的Field对象,Class类与Field对象相关方法如下:
Field
getDeclaredField(String name)
获取指定name名称的(包含private修饰的)字段,不包括继承的字段
Field[]
getDeclaredField()
获取Class对象所表示的类或接口的所有(包含private修饰的)字段,不包括继承的字段
Field
getField(String name)
获取指定name名称、具有public修饰的字段,包含继承字段
Field[]
getField()
获取修饰符为public的字段,包含继承字段
下面的代码演示了上述方法的使用过程:
上述方法需要注意的是,如果我们不期望获取其父类的字段,则需使用Class类的getDeclaredField/getDeclaredFields方法来获取字段即可,倘若需要连带获取到父类的字段,那么请使用Class类的getField/getFields,但是也只能获取到public修饰的的字段,无法获取父类的私有字段。下面将通过Field类本身的方法对指定类属性赋值,代码演示如下:
其中的set(Object obj, Object value)方法是Field类本身的方法,用于设置字段的值,而get(Object obj)则是获取字段的值,当然关于Field类还有其他常用的方法如下:
著作权归https://www.pdai.tech所有。 链接:https://www.pdai.tech/md/java/basic/java-basic-x-reflection.html
void
set(Object obj, Object value)
将指定对象变量上此 Field 对象表示的字段设置为指定的新值。
Object
get(Object obj)
返回指定对象上此 Field 表示的字段的值
Class<?>
getType()
返回一个 Class 对象,它标识了此Field 对象所表示字段的声明类型。
boolean
isEnumConstant()
如果此字段表示枚举类型的元素则返回 true;否则返回 false
String
toGenericString()
返回一个描述此 Field(包括其一般类型)的字符串
String
getName()
返回此 Field 对象表示的字段的名称
Class<?>
getDeclaringClass()
返回表示类或接口的 Class 对象,该类或接口声明由此 Field 对象表示的字段
void
setAccessible(boolean flag)
将此对象的 accessible 标志设置为指示的布尔值,即设置其可访问性
上述方法可能是较为常用的,事实上在设置值的方法上,Field类还提供了专门针对基本数据类型的方法,如setInt()/getInt()、setBoolean()/getBoolean、setChar()/getChar()等等方法,这里就不全部列出了,需要时查API文档即可。需要特别注意的是被final关键字修饰的Field字段是安全的,在运行时可以接收任何修改,但最终其实际值是不会发生改变的。
2.4 Method类及其用法
Method 提供关于类或接口上单独某个方法(以及如何访问该方法)的信息,所反映的方法可能是类方法或实例方法(包括抽象方法)。
下面是Class类获取Method对象相关的方法:
Method
getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
返回一个指定参数的Method对象,该对象反映此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口的指定已声明方法。
Method[]
getDeclaredMethod()
返回 Method 对象的一个数组,这些对象反映此 Class 对象表示的类或接口声明的所有方法,包括公共、保护、默认(包)访问和私有方法,但不包括继承的方法。
Method
getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
返回一个 Method 对象,它反映此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口的指定公共成员方法。
Method[]
getMethods()
返回一个包含某些 Method 对象的数组,这些对象反映此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口(包括那些由该类或接口声明的以及从超类和超接口继承的那些的类或接口)的公共 member 方法。
同样通过案例演示上述方法:
输出结果:
在通过getMethods方法获取Method对象时,会把父类的方法也获取到,如上的输出结果,把Object类的方法都打印出来了。而getDeclaredMethod/getDeclaredMethods方法都只能获取当前类的方法。我们在使用时根据情况选择即可。下面将演示通过Method对象调用指定类的方法:
输出结果:
在上述代码中调用方法,使用了Method类的invoke(Object obj,Object... args)第一个参数代表调用的对象,第二个参数传递的调用方法的参数。这样就完成了类方法的动态调用。
Object
invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
对带有指定参数的指定对象调用由此 Method 对象表示的底层方法。
Class<?>
getReturnType()
返回一个 Class 对象,该对象描述了此 Method 对象所表示的方法的正式返回类型,即方法的返回类型
Type
getGenericReturnType()
返回表示由此 Method 对象所表示方法的正式返回类型的 Type 对象,也是方法的返回类型。
Class<?>[]
getParameterTypes()
按照声明顺序返回 Class 对象的数组,这些对象描述了此 Method 对象所表示的方法的形参类型。即返回方法的参数类型组成的数组
Type[]
getGenericParameterTypes()
按照声明顺序返回 Type 对象的数组,这些对象描述了此 Method 对象所表示的方法的形参类型的,也是返回方法的参数类型
String
getName()
以 String 形式返回此 Method 对象表示的方法名称,即返回方法的名称
boolean
isVarArgs()
判断方法是否带可变参数,如果将此方法声明为带有可变数量的参数,则返回 true;否则,返回 false。
String
toGenericString()
返回描述此 Method 的字符串,包括类型参数。
getReturnType方法/getGenericReturnType方法都是获取Method对象表示的方法的返回类型,只不过前者返回的Class类型后者返回的Type(前面已分析过),Type就是一个接口而已,在Java8中新增一个默认的方法实现,返回的就参数类型信息。
而getParameterTypes/getGenericParameterTypes也是同样的道理,都是获取Method对象所表示的方法的参数类型,其他方法与前面的Field和Constructor是类似的。
3. 反射机制执行的流程
这部分主要参考自https://www.cnblogs.com/yougewe/p/10125073.html
先看个例子:
来看执行流程:
3.1 反射获取类实例
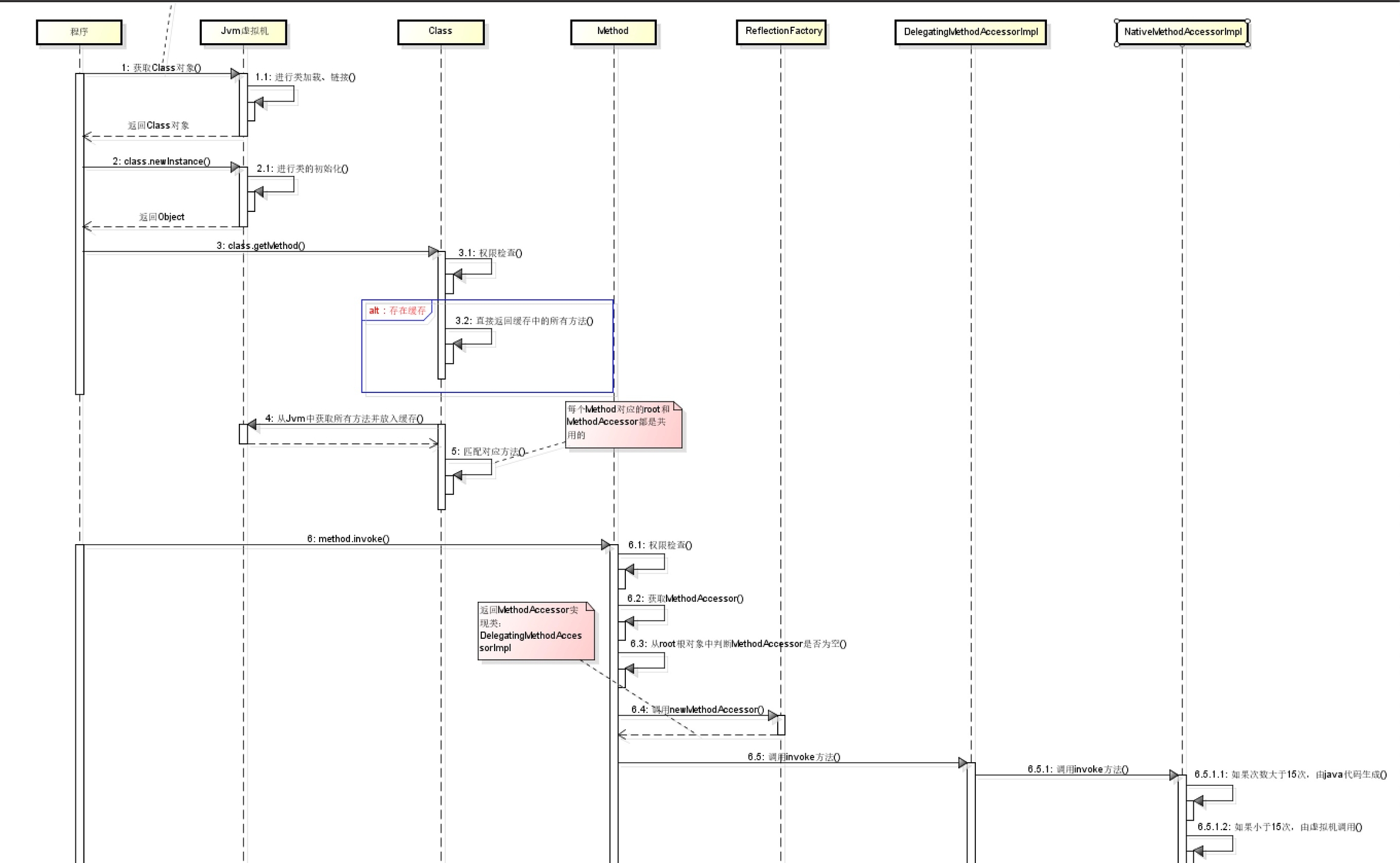
首先调用了 java.lang.Class 的静态方法,获取类信息。
forName()反射获取类信息,并没有将实现留给了java,而是交给了jvm去加载。
主要是先获取 ClassLoader, 然后调用 native 方法,获取信息,加载类则是回调 java.lang.ClassLoader.
最后,jvm又会回调 ClassLoader 进类加载。
下面来看一下 newInstance() 的实现方式。
newInstance() 主要做了三件事:
权限检测,如果不通过直接抛出异常;
查找无参构造器,并将其缓存起来;
调用具体方法的无参构造方法,生成实例并返回;
下面是获取构造器的过程:
getConstructor0() 为获取匹配的构造方器;分三步:
先获取所有的constructors, 然后通过进行参数类型比较;
找到匹配后,通过 ReflectionFactory copy一份constructor返回;
否则抛出 NoSuchMethodException;
如上,privateGetDeclaredConstructors(), 获取所有的构造器主要步骤;
先尝试从缓存中获取;
如果缓存没有,则从jvm中重新获取,并存入缓存,缓存使用软引用进行保存,保证内存可用;
另外,使用 relactionData() 进行缓存保存;ReflectionData 的数据结构如下。
其中,还有一个点,就是如何比较构造是否是要查找构造器,其实就是比较类型完成相等就完了,有一个不相等则返回false。
通过上面,获取到 Constructor 了。
接下来就只需调用其相应构造器的 newInstance(),即返回实例了。
返回构造器的实例后,可以根据外部进行进行类型转换,从而使用接口或方法进行调用实例功能了。
3.2 反射获取方法
第一步,先获取 Method;
忽略第一个检查权限,剩下就只有两个动作了。
获取所有方法列表;
根据方法名称和方法列表,选出符合要求的方法;
如果没有找到相应方法,抛出异常,否则返回对应方法;
所以,先看一下怎样获取类声明的所有方法?
很相似,和获取所有构造器的方法很相似,都是先从缓存中获取方法,如果没有,则从jvm中获取。
不同的是,方法列表需要进行过滤 Reflection.filterMethods;当然后面看来,这个方法我们一般不会派上用场。
第二步,根据方法名和参数类型过滤指定方法返回:
大概意思看得明白,就是匹配到方法名,然后参数类型匹配,才可以。
但是可以看到,匹配到一个方法,并没有退出for循环,而是继续进行匹配。
这里是匹配最精确的子类进行返回(最优匹配)
最后,还是通过 ReflectionFactory, copy 方法后返回。
3.3 调用 method.invoke() 方法
invoke时,是通过 MethodAccessor 进行调用的,而 MethodAccessor 是个接口,在第一次时调用 acquireMethodAccessor() 进行新创建。
两个Accessor详情:
进行 ma.invoke(obj, args); 调用时,调用 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke();
最后被委托到 NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(), 即:
其中, generateMethod() 是生成具体类的方法:
generate() 戳详情。
咱们主要看这一句:ClassDefiner.defineClass(xx, declaringClass.getClassLoader()).newInstance();
在ClassDefiner.defineClass方法实现中,每被调用一次都会生成一个DelegatingClassLoader类加载器对象 ,这里每次都生成新的类加载器,是为了性能考虑,在某些情况下可以卸载这些生成的类,因为类的卸载是只有在类加载器可以被回收的情况下才会被回收的,如果用了原来的类加载器,那可能导致这些新创建的类一直无法被卸载。
而反射生成的类,有时候可能用了就可以卸载了,所以使用其独立的类加载器,从而使得更容易控制反射类的生命周期。
3.4 反射调用流程小结
最后,用几句话总结反射的实现原理:
反射类及反射方法的获取,都是通过从列表中搜寻查找匹配的方法,所以查找性能会随类的大小方法多少而变化;
每个类都会有一个与之对应的Class实例,从而每个类都可以获取method反射方法,并作用到其他实例身上;
反射也是考虑了线程安全的,放心使用;
反射使用软引用relectionData缓存class信息,避免每次重新从jvm获取带来的开销;
反射调用多次生成新代理Accessor, 而通过字节码生存的则考虑了卸载功能,所以会使用独立的类加载器;
当找到需要的方法,都会copy一份出来,而不是使用原来的实例,从而保证数据隔离;
调度反射方法,最终是由jvm执行invoke0()执行;
4. 反射的使用场景
4.1 JDBC 的数据库的连接
在JDBC 的操作中,如果要想进行数据库的连接,则必须按照以上的几步完成:
通过
Class.forName()加载数据库的驱动程序 (通过反射加载,前提是引入相关了Jar包)通过 DriverManager 类进行数据库的连接,连接的时候要输入数据库的连接地址、用户名、密码
通过Connection 接口接收连接。
4.2 Spring 框架
根据配置文件加载不同的类或对象(运行期间,动态加载所需对象)。
4.3 序列化/反序列化
序列化是将对象转换为容易传输的格式的过程,比如转化为二进制、xml、json从而在网络中传输。与序列化相反的是反序列化,它将流转换为对象,也就是将在序列化过程中所产生的二进制串、XML、Json等转换成数据结构或对象的过程。将序列化和反序列化两个过程接合起来,可以轻松地存储、传输数据。
反序列化都是通过反射实现的。
5. 反射的优缺点
反射在运行时判断,动态创建对象,提高代码的灵活度。但一般情况下,并不是我们优先建议的,主要原因是:
反射更容易出现运行时错误,使用显式的类和接口,编译器能帮我们做类型检查,减少错误,但使用反射,类型是运行时才知道的,编译器无能为力。
反射的性能要低一些,在访问字段、调用方法前,反射先要查找对应的Field/Method,性能要慢一些。
简单的说,如果能用接口实现同样的灵活性,就不要使用反射。
6. 参考
https://www.codercto.com/a/46094.html
https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_38259539/article/details/71799078
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40896997/article/details/94483820
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaoguhong/p/6937364.html
https://juejin.im/post/5c160420e51d452a60684431
https://blog.csdn.net/mcryeasy/java/article/details/52344729
最后更新于